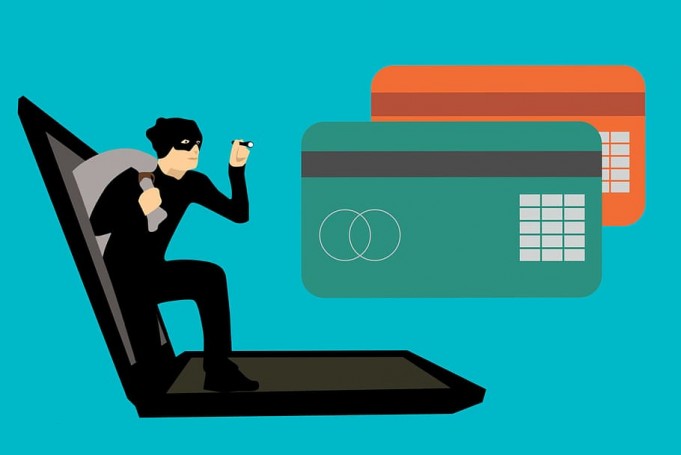
Millions of Americans fall victim to identity theft each year. Identity theft occurs when someone illegally acquires your Personally Identifiable Information (PII), which is later used to commit fraud. Identity theft can happen in numerous ways. However, most fraudsters use the internet to commit identity theft frauds.
Fraudsters can access your digital PII by planting malware on your personal computer. An individual’s digital PII (Personally Identifiable Information) contains a lot of sensitive information. This information includes your bank account numbers and driver’s license. These are unique pieces of information that are used to identify you. Once fraudsters gain access to your Personally Identifiable Information, they might present themselves as you. They may make claims for financial benefits in which you are entitled. For example, if a fraudster acquires your social security number, it is possible that he/she could apply for a tax refund or file employment forms in your name.
Types of Online Identity Theft
Phishing
Phishing is a cybercrime that is used by fraudsters in order to acquire personal information from people. In phishing, the victim receives e-mails from the fraudsters, who deceive themselves as a trusted organization. In most cases, the victim receives an e-mail, which appears to be from a financial institution. The victim is then manipulated into clicking on the links that these e-mails provide. The victim ultimately ends up sharing his/her sensitive personal information. Thus acquired information is later exploited for financial scams later on.
To protect yourself from phishing, ignore unsolicited spam e-mails. If you want to access the website of a financial institution, ensure the safety of the website before logging in. Always type in the URL of the website in the address bar of your browser, rather than clicking on unknown e-mails.
Pharming
Pharming is another type of cyber-attack aimed at stealing your personal information. However, in this case, your web browser is infected by a virus. Even if you type in the URL of a trusted website, the browser redirects you to a scam website. This website might appear legitimate. Fraudsters can easily compile the personal information that you type in this website. Unsecured websites can easily take away your personal information. Secure websites carry the prefix “https” in their URL. Websites whose prefixes are “HTTP” are not secure.
Malware
A malware attack is another method used by fraudsters and cybercriminals to steal personal information of an individual. The user may be tricked into downloading malware, which is often disguised as genuine software. This software can attack your personal computer and ultimately expose your personal information to fraudsters. It is always recommended to buy genuine versions of the software. If you are downloading the software online, make sure that you are downloading it from a trusted website.
While discarding or selling your old device, make sure that the device is formatted so that you do not reveal your personal information. Always keep your software up-to-date. Setting up a firewall and installing antivirus software is also highly recommended. If children are using any internet-connected device, make sure that the information that they share is monitored by adults.